Bys-sáma
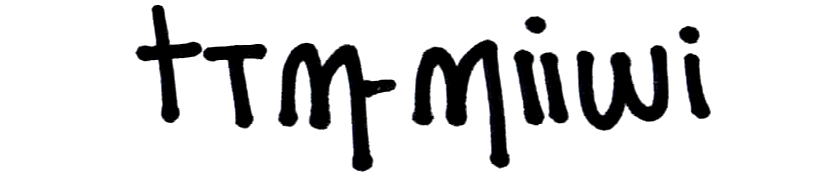
| DATE | 2006-2016 |
| GENERAL RULES |
Simplified relative of Xema Two vowels can't follow each other (sénsa tha alén becomes sénsa th'alén) |
| RELATED |
Eloa world-building page Xema Aŝan Rac,mamoqei |
While Xema was spoken for a long time among the Elvish upperclass, it was not suited for simple everyday use. Bys-sáma ("New Xema") developed from informal Xema and ultimately became the most widely-spoken language throughout the Tippan Empire.
Phonology
Bys-sáma brought with it a sound shift that gave the language a rougher sound in comparison to its softer predecessor.
| XEMA | → | BYS-SÁMA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LETTER | SOUND | LETTER | SOUND | |
| x | z | → | ś | ʃ |
| th | θ | → | t | t |
| p | p | → | b | b |
| h | h | → | ģ | x |
| u | → | ú o |
||
| e | → | á | ||
| i | → | e é |
||
| ii | → | é | ||
Pronouns
- Bys-sáma loses Xema's overly complicated pronoun system but retains some aspects.
- Bys-sáma also loses all cases except for object di- (combining accusative and dative), genitive ti-, and instrumental ni-.
| subject | I | you | they | it | we |
| basic/ topic of discussion* |
alyn | ǵal | dún | sat | mén |
| casual | ale | ǵon | de | se | me |
| superior | alant | ǵant | dúnt | sant | mént |
| many | alene | ǵene | dene | sene | mene |
Verbs
- Infinitive have no specific suffix and tense is simply added to the infinitive.
- Don't conjugate according to person (eg. xalthasu salwin, "I am"; xalthasu sidurn, "they are").
- A negative is indicated by a ko- prefix, retained from Xema.
| AFFIX | TENSE | EXAMPLE |
| -su | present | śaltsu alyn, "I am" |
| -śe | near future | śaltśe alyn, "I will be soon" |
| -tú | distant future | śaltú alyn, "I will be one day" |
| -né | near past | śaltné alyn, "I was recently" |
| -to | distant past | śalto alyn, "I was long ago" |
| -be | present conditional | śaltbe alyn, "I would be" |
| -nab | past conditional | śaltnab alyn, "I would have been" |
| -ma | present progressive | śaltma alyn, "I am being" |
| -tema | future progressive | śaltema alyn, "I will be being" |
| -nama | past progressive | śaltnama, "I was being" |
| none | imperative | śalt, "be!" |
Example Sentences
-
English: Did they see us?
Bys-sáma: ham nakéné dún dimén
Transliteration: question see.past they(BASIC) accusative.us(BASIC) -
English: We made it for you (superior).
Bys-sáma: kúnané disat má ǵant mén
Transliteration: make.past accusative.it(TOPIC) for you(SUPERIOR) we(BASIC)
My candle burns at both ends;
It will not last the night;
But ah, my foes, and oh, my friends--
It gives a lovely light!
| XEMA | BYS-SÁMA |
|
matiinansu kidiibiino dis sisiinsa thalwon; konosonxe kisune sisath; nadiindona thalwon, nadiinkarna thalwon, keme-- saninansu tidasani akos sisath! |
madimsu ká débém dés sénsa talyn; konosośe ká súm sat; détona talyn, déǵana talyn, keme-- saninasu ditasan akos sat! |
|
2nd line: negative.last(V).near-future locative.night nominative.it(TOPIC) 3rd line: vocative.many.enemy genitive.I, vocative.many.friend genitive.I, despite-this 4th line: give.present accusative.light lovely nominative.it(TOPIC) |
2nd line: negative.last(V).near-future at night it(TOPIC) 3rd line: multiple.enemy genitive.I, multiple.friend genitive.I, despite-this 4th line: give.present accusative.light lovely it(TOPIC) |
Writing system

Writing examples
